The Argos locations
 Argonautica provides Argos beacon positions each week on the web site. These positions are obtained using satellites carrying the Argos instrument which locates beacons transmitting from the Earth's surface. Three satellite passes are required to obtain a good fix. More information can be found at Argos: How it works on the CLS web site.
Argonautica provides Argos beacon positions each week on the web site. These positions are obtained using satellites carrying the Argos instrument which locates beacons transmitting from the Earth's surface. Three satellite passes are required to obtain a good fix. More information can be found at Argos: How it works on the CLS web site.
An Argos beacon may also contain sensors that measure temperature, pressure, etc. in its immediate environment.
Animal transmitters are designed by biologists and placed in such a way as to hamper the animal as little as possible (the idea being that the animal should behave normally in order to study its way of life).
The Argos processing centre collects and processes locations and other measurements prior to sending it to the scientists who had either attached a transmitter to an animal or launched a beacon at sea in order to collect the data.
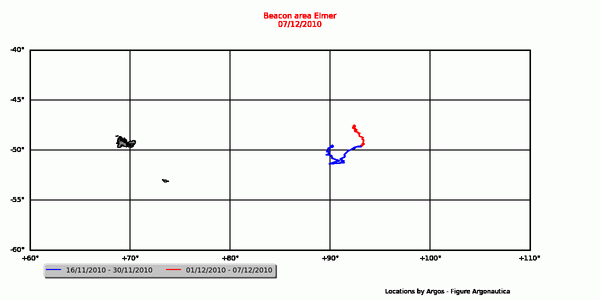
The location positions provided by Argonautica
Argonautica simplifies and homogenises the Argos files it receives: among all the data provided by Argos, only a small amount is maintained; all data are presented in an identical format.
Weekly positions are provided beacon by beacon in table format. A text file, as displayed on the web page, can be downloaded with the table.
The name of weekly location files incorporates the date at the end of each weekly period. For example, location positions in the aronnax_2004-11-30.txt file start on 24 November 2004 and end on 30 November 2004 inclusive. Another file is available and contains all of the locations since the Argonautica tracking of the beacon began.
Moreover, the locations are given and dated point by point in the Google Earth file of the beacon.
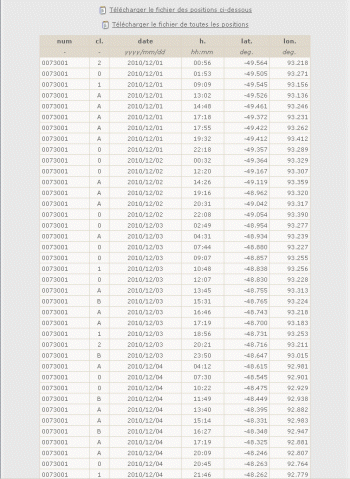
| - Num.: | Each beacon has a number, rather than a name, in the Argos system. The unique number means it can be identified among the approximately 20000 operational beacons so that the right positions can be sent to the right person. It is provided by Argonautica for information only and can be ignored.
|
| - cl.: | This indicator (1, 2 or 3) gives the "confidence" we have in the location with 3 being the highest (then 2, 1, sometimes 0). Indeed, several phenomena can deteriorate positioning (for example, being seen by only twice by a satellite instead of three times). All figures correspond to a message recorded at least 4 times by a satellite. 3 is an estimated error below 250 m, 2 between 250 m & 500 m, 1 between 500 m & 1500 m, 0 (if any) above 1500 m. For marine animal location, which is more difficult than for buoys (animals can be more or less under water, dive before the end of the transmission, etc. and, to reduce weight, transmitters are less powerful), other indicators, A and B are also used (indicating locations we are even less sure of; A corresponds to a message recorded only three times by a satellite, B only once or twice). The letter Z is always a "bad" (invalid) location, to be removed if it has been kept (keeping it can be requested by the scientists who use the data) If locations indicated as 1, 2 or 3 are in a large majority, A or especially B-flagged locations can be removed / not taken into account. If (as is often the case with marine animals), locations are mostly "A" or "B", it is better to keep them. You can then compute the distance traveled between two points, or the speed between those two points to estimate whether or not a location is erroneous and delete it, or look at whether or not a point is in the continuity of the path traveled before and after. |
| - date: | Dates are given in year / month / day which is the "international" format for date data. |
| - h.: | Time is given in hours, minutes, hh:mm: UTC (Universal Time Coordinated); Universal time frees us from time zones or changes from summer to winter time. In France, the time zone is UTC+1 h in winter, UTC+2 h in Summer. |
| - lat.: | Latitude, in degrees (from -90° at the South Pole to +90° at the North Pole) and in thousandths of degrees (instead of degrees, minutes and seconds). |
| - lon.: | Longitude, in degrees (from 0 to -180° going west and 0 to 180° going East) and in thousandths of degrees (instead of degrees, minutes and seconds). |
| Pressure, in HectoPascal (HPa), if a beacon sensor was programmed to measure it and if the measurements are available for Argonautica. |
|
| - temp.: | Temperature, in Celsius (°C), if a beacon sensor was programmed to measure it and if the measurements are available for Argonautica. |

